Operational Permits
Permits required. A property owner or owner’s authorized agent who intends to conduct an operation or business, or install or modify systems and equipment that are regulated by this code, or to cause any such work to be performed, shall first make application to the fire code official and obtain the required permit. (IFC 105.1.1)
Operational permit. An operational permit allows the applicant to conduct an operation or a business for which a permit is required by IFC Section 105.5. (IFC 105.1.2)
Operational permits shall be valid for a period of time not to exceed 365 days, or until the expiration date posted on the permit, whichever comes first.
Inspection authorized. Before a new operational permit is approved, the fire code official is authorized to inspect the receptacles, vehicles, buildings, devices, premises, storage spaces or areas to be used to determine compliance with this code or any operational constraints required. (IFC 105.2.2)
Definitions. Definitions are identified in the International Fire Code, International Building Code, or other ICC documents.
Re-inspection fees may apply. If an inspector has to return due to an incomplete or failed inspection, re-inspection may be assessed. Re-inspection fees are as follows:
- First re-inspection = $75
- Second re-inspection = $150
- Third and subsequent re-inspections = $300
An operational permit is required to operate a special amusement building. (IFC 105.5.3)
SPECIAL AMUSEMENT BUILDING. A building that is temporary, permanent or mobile that contains a device or system that conveys passengers or provides a walkway along, around or over a course in any direction as a form of amusement arranged so that the egress path is not readily apparent due to visual or audio distractions or an intentionally confounded egress path, or is not readily available because of the mode of conveyance through the building or structure. (IFC 202)
An operational permit is required to conduct a carnival or fair. (IFC 105.5.5)
An operational permit is required to operate exhibits and trade shows. (IFC 105.5.15)
An operational permit is required to operate a grain elevator, flour starch mill, feed mill, or a plant pulverizing aluminum, coal, cocoa, magnesium, spices or sugar, or other operations producing combustible dusts as defined in Chapter 2. (IFC 105.5.7)
An operational permit is required for the storage and handling of combustible fibers in quantities greater than 100 cubic feet (2.8 m3). Exception: A permit is not required for agricultural storage. (IFC 105.5.8)
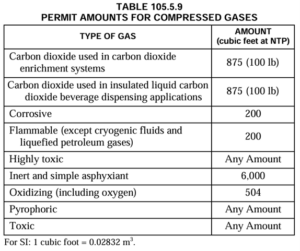
An operational permit is required for the storage, use or handling at normal temperature and pressure (NTP) of compressed gases in excess of the amounts listed in Table 105.5.9. Exception: Vehicles equipped for and using compressed gas as a fuel for propelling the vehicle. (IFC 105.5.9)
An operational permit is required to produce, store, transport on site, use, handle or dispense cryogenic fluids in excess of the amounts listed in Table 105.5.11. (IFC 105.5.11)

An operational permit is required to conduct cutting or welding operations within the jurisdiction. (IFC 105.5.12)
An operational permit is required for hot work including, but not limited to:
- Public exhibitions and demonstrations where hot work is conducted.
- Use of portable hot work equipment inside a structure. Exception: Work that is conducted under a construction permit.
- Fixed-site hot work equipment, such as welding booths.
- Hot work conducted within a wildfire risk area.
- Application of roof coverings with the use of an open-flame device.
- Where approved, the fire code official shall issue a permit to carry out a hot work program. This program allows approved personnel to regulate their facility’s hot work operations. The approved personnel shall be trained in the fire safety aspects denoted in this chapter and shall be responsible for issuing permits requiring compliance with the requirements found in Chapter 35. These permits shall be issued only to their employees or hot work operations under their supervision. (IFC 105.5.25)
An operational permit is required to remove paint with a torch, or to use a torch or open-flame device in a wildfire risk area. (IFC 105.5.35)
An operational permit is required for stationary and mobile energy storage systems regulated by Section 1207. (IFC 105.5.14)
ENERGY STORAGE SYSTEM (ESS). One or more devices, assembled together, capable of storing energy in order to supply electrical energy at a future time. (IFC 202)
An operational permit is required for the manufacture, storage, handling, sale or use of any quantity of explosives, explosive materials, fireworks or pyrotechnic special effects within the scope of Chapter 56. (IFC 105.5.16)
An operational permit is required for use and handling of pyrotechnic special effects material. (IFC 105.5.42)
An operational permit is required for the manufacture, storage, handling, sale or use of any quantity of explosives, explosive materials, fireworks or pyrotechnic special effects within the scope of Chapter 56. (IFC 105.5.16)
An operational permit is required:
- To use or operate a pipeline for the transportation within facilities of flammable or combustible liquids. This requirement shall not apply to the off-site transportation in pipelines regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOTn) nor does it apply to piping systems.
- To store, handle or use Class I liquids in excess of 5 gallons (19 L) in a building or in excess of 10 gallons (37.9 L) outside of a building, except that a permit is not required for the following:
2.1. The storage or use of Class I liquids in the fuel tank of a motor vehicle, aircraft, motorboat, mobile power plant or mobile heating plant, unless such storage, in the opinion of the fire code official, would cause an unsafe condition.
2.2. The storage or use of paints, oils, varnishes or similar flammable mixtures where such liquids are stored for maintenance, painting or similar purposes for a period of not more than 30 days.
- To store, handle or use Class II or Class IIIA liquids in excess of 25 gallons (95 L) in a building or in excess of 60 gallons (227 L) outside a building, except for fuel oil used in connection with oil burning equipment.
- To store, handle or use Class IIIB liquids in tanks or portable tanks for fueling motor vehicles at motor fuel-dispensing facilities or where connected to fuel-burning equipment. Exception: Fuel oil and used motor oil used for space heating or water heating.
- To remove Class I or II liquids from an underground storage tank used for fueling motor vehicles by any means other than the approved, stationary on-site pumps normally used for dispensing purposes.
- To operate tank vehicles, equipment, tanks, plants, terminals, wells, fuel-dispensing stations, refineries, distilleries and similar facilities where flammable and combustible liquids are produced, processed, transported, stored, dispensed or used.
- To place temporarily out of service (for more than 90 days) an underground, protected above-ground or above-ground flammable or combustible liquid tank.
- To change the type of contents stored in a flammable or combustible liquid tank to a material that poses a greater hazard than that for which the tank was designed and constructed.
- To manufacture, process, blend or refine flammable or combustible liquids.
- To engage in the dispensing of liquid fuels into the fuel tanks of motor vehicles at commercial, industrial, governmental or manufacturing establishments in accordance with Section 5706.5.4 or to engage in on-demand mobile fueling operations in accordance with Section 5707.
- To utilize a site for the dispensing of liquid fuels from tank vehicles into the fuel tanks of motor vehicles, marine craft and other special equipment at commercial, industrial, governmental or manufacturing establishments in accordance with Section 5706.5.4 or, where required by the fire code official, to utilize a site for on-demand mobile fueling operations in accordance with Section 5707.
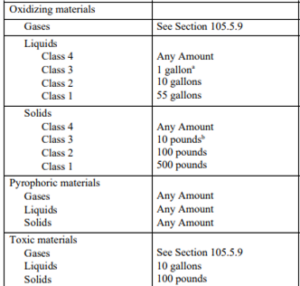
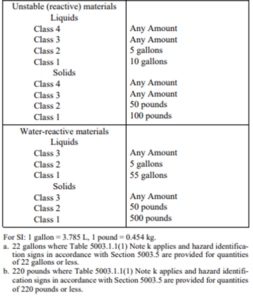
An operational permit is required to store, transport on site, dispense, use or handle hazardous materials in excess of the amounts listed in Table 105.5.22. (IFC 105.5.22)

An operational permit is required to store, handle or use hazardous production materials. (IFC 105.5.23)
An operational permit is required to use a building or portion thereof with more than 500 square feet (46 m2), including aisles, of high piled combustible storage. (IFC 105.5.24)
HIGH-PILED COMBUSTIBLE STORAGE. Storage of combustible materials in closely packed piles or combustible materials on pallets, in racks or on shelves where the top of storage is greater than 12 feet in height. Where required by the fire code official, high-piled combustible storage also includes certain high-hazard commodities, such as rubber tires, Group A plastics, flammable liquids, idle pallets and similar commodities, where the top of storage is greater than 6 feet in height. (IFC 202)
An operational permit is required for the storage or processing of lumber exceeding 100,000 board feet (8,333 ft3) (236 m3). (IFC 105.5.27)
An operational permit is required for:
- Storage and use of LP-gas. Exception: A permit is not required for individual containers with a 500-gallon (1893 L) water capacity or less or multiple container systems having an aggregate quantity not exceeding 500 gallons (1893 L), serving occupancies in Group R-3.
- Operation of cargo tankers that transport LP-gas. (IFC 105.5.29)
A permit is required for mobile food preparation vehicles equipped with appliances that produce smoke or grease-laden vapors. (IFC 105.5.32) A permit is required for any mobile food preparation vehicles operated inside the city limits of Kyle. (CoK) (IFC 105.5.32)
An operational permit is required for the operation of automotive, marine and fleet motor fuel-dispensing facilities. (IFC 105.5.33)
An operational permit is required for the kindling or maintaining of an open fire or a fire on any public street, alley, road, or other public or private ground. Instructions and stipulations of the permit shall be complied with. Exception: Recreational fires. (IFC 105.5.34)
An operational permit is required to use open flames or candles in connection with assembly areas, dining areas of restaurants or drinking establishments where the buildings are not sprinklered. (IFC 105.5.36)
An operational permit is required to conduct an outdoor assembly event where planned attendance exceeds 1,000 persons. (IFC 105.5.38) NOTE: Where outdoor events involve a gathering of more than 1000 people, crowd managers shall be provided in accordance with International Fire Code Sections 403.11.3.1 through 403.11.3.3. Not fewer than one trained crowd manager for each 250 persons or portion thereof, shall be provided for the gathering. Outdoor events with fewer than 1,000 persons in attendance shall not require crowd managers. (IFC 403.11.3)
An operational permit is required to operate a place of assembly with greater than 99-person occupancy. Includes Indoor Assembly Events where planned attendance exceeds 500 persons. (IFC 105.5.39) NOTE: Where facilities or events involve a gathering of more than 500 people, crowd managers shall be provided in accordance with International Fire Code Sections 403.11.3.1 through 403.11.3.3. (IFC 403.11.3)
An operational permit is required to use plant extraction systems. (IFC 105.5.40)
An operational permit is required for operation of repair garages.
An operational permit is required for the operation of a rooftop heliport. (IFC 105.5.46)
HELIPORT. An area of land or water or a structural surface that is used, or intended for use, for the landing and taking off of helicopters, and any appurtenant areas which are used, or intended for use, for heliport buildings and other heliport facilities. (IFC 202)
An operational permit is required for the operation of a helistop.
HELISTOP. The same as “Heliport,” except that fueling, defueling, maintenance, repairs or storage of helicopters is not permitted. (IFC 202)
An operational permit is required to conduct a spraying or dipping operation utilizing flammable or combustible liquids, or the application of combustible powders regulated by Chapter 24. (IFC 105.5.47)
An operational permit is required to establish, conduct or maintain storage of scrap tires and tire byproducts that exceeds 2,500 cubic feet (71 m3) of total volume of scrap tires, and for indoor storage of tires and tire byproducts. (IFC 105.5.48)
An operational permit is required to operate an air supported temporary membrane structure, a temporary special event structure or a tent having an area in excess of 400 square feet (37 m2).
Exceptions:
- Tents used exclusively for recreational camping purposes.
- Tents open on all sides, which comply with all of the following:
- Individual tents having a maximum size of 700 square feet (65 m2).
- The aggregate area of multiple tents placed side by side without a fire break clearance of not less than 12 feet (3658 mm) shall not exceed 700 square feet (65 m2) total.
- A minimum clearance of 12 feet (3658 mm) to structures and other tents shall be provided.
IFC Section 105.5 Operational Permit that is not specifically noted in this fee schedule. Refer to IFC 105.5 Required Operational Permits for additional information.
Applies to any permit-required operation that is performed without a permit. If the fire department identifies operations being performed that should have been permitted according to IFC Section 105, then that work shall cease, and the owner, operator or designee shall submit a request for a permit to perform such operation. The fire department may assess an “Operating without a Permit” Fee to the permit application.


